Summary:
This definitive guide explores the "Japanese Progression" (IV–V–iii–vi), the iconic chord sequence that gives J-pop, anime themes, and video game music its signature emotional power. We deconstruct its music theory, analyze the harmonic "trick" that makes it so effective, and provide interactive MusicXML examples and practical tips to help you recognize it in your favorite media and use it in your own compositions.
Keywords:
Japanese progression, chord progression, music theory, harmony, IV-V-iii-vi, anime music, J-pop, video game music, diatonic chords, songwriting, music analysis, Royal Road Progression
Introduction:
Have you ever felt a rush of uplifting, yet bittersweet emotion from an anime opening? Or noticed a familiar, hopeful feeling in the chorus of a J-pop anthem or an epic video game theme? That powerful sensation is often a deliberate choice, crafted with one of the most effective tools in modern pop music: a sequence of chords known in the West as the "Japanese Progression." While not exclusive to Japan, its masterful and frequent use in Japanese media has made it an unmistakable sonic signature. This guide will take you on a deep dive into the theory, emotional impact, and practical application of this beloved progression.
What Is the Japanese Progression?
The Japanese Progression is a diatonic chord progression built from the major scale. Its most common form uses the fourth, fifth, third, and sixth chords of the scale, creating the sequence **IV–V–iii–vi**. Let's break this down using the key of C Major as our reference:
- IV: The Subdominant - F Major (F–A–C). This chord provides a gentle "lift-off" from the home base (I, or C Major), creating a sense of hopeful departure.
- V: The Dominant - G Major (G–B–D). The dominant chord creates strong harmonic tension. It builds anticipation and makes the listener expect a satisfying resolution back to the tonic (I).
- iii: The Mediant (The Twist!) - E minor (E–G–B). Here is the progression's secret weapon. Instead of resolving the tension as expected (V → I), it moves to the minor mediant chord. This is a type of "deceptive resolution." The iii chord (E minor) is a clever substitute for the I chord (C Major) because they share two notes (E and G). This shared DNA makes the transition feel smooth, yet the minor quality introduces a sudden, poignant shift in mood—the source of that signature "bittersweet" feeling.
- vi: The Submediant - A minor (A–C–E). The progression finally lands on the relative minor of the original key. This chord confirms the slightly melancholic, introspective mood introduced by the iii chord, leaving the listener in a state of hopeful reflection before the progression often loops back to the IV chord.
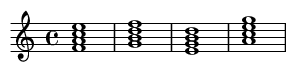
Hearing It in Action: MusicXML Examples
1. The Classic Progression (IV–V–iii–vi)
Here are the four chords in their basic form in C Major. Listen for the emotional journey from the hopeful IV chord to the melancholic vi chord. Roman numerals are included below each measure for analysis.

2. Adding Flavor with Seventh Chords
Composers frequently add seventh chords to create a richer, more complex sound. This version (IVmaj7–V7–iii7–vi7) is extremely common in city pop, anime themes, and jazz-influenced video game music.
How to Use It: A Songwriter's Guide
Recognizing the progression is one thing; using it is another. Here are some tips for incorporating it into your own music:
- The Chorus is Key: Its emotional payoff makes it perfect for a song's chorus, creating a memorable and impactful peak.
- Melody Matters: When writing a melody over the progression, try to emphasize the unique notes of each chord. For instance, holding a B over the E minor (iii) chord will highlight the melancholic shift away from the expected C Major resolution.
- Experiment with Rhythm: Don't just play block chords. Break them up into arpeggios or create syncopated rhythmic patterns to give the progression energy and movement.
Below is a simple melodic idea over the progression to show how the harmony and melody can work together. The left hand plays the chord roots while the right hand plays a simple melody.

Famous Examples and Historical Context
This progression is everywhere in Japanese media. You can hear its classic form or slight variations in the iconic opening "A Cruel Angel's Thesis" from *Neon Genesis Evangelion* and "God knows..." from *The Melancholy of Haruhi Suzumiya*. It's a staple in the work of legendary video game composer **Nobuo Uematsu** (*Final Fantasy* series) and the genre-bending scores of **Yoko Kanno** (*Cowboy Bebop*, *Ghost in the Shell*). These composers didn't "invent" the progression, but they helped codify an emotional language that made it a cornerstone of Japanese pop culture music.
Fun Facts: The "Royal Road"
Interestingly, the name "Japanese Progression" is largely a Western term, coined by fans and analysts. In Japan, it is often simply called by its numbers, "yon-go-san-roku" (四五三六 or 4-5-3-6). This progression is also the first half of a longer, even more famous sequence known as the **"Ōdō Shinkō" (王道進行)**, which translates to the "Royal Road" or "Golden Route" progression. This sequence, **IV–V–iii–vi–ii–V–I**, is considered a surefire formula for writing a hit song chorus in J-pop.
Conclusion: Your Turn to Listen
The Japanese Progression (IV–V–iii–vi) is more than a series of chords; it's a powerful storytelling device. Its genius lies in building expectation with the V chord and then delivering an emotional surprise with the iii chord, creating a complex feeling of nostalgia, determination, and bittersweet hope. By understanding its structure, you not only gain a deeper appreciation for the soundtracks and songs you love, but you also unlock a potent tool for your own creative arsenal. Now that you know the secret, go listen to your favorite anime theme or J-pop track. Can you hear the Royal Road calling?
References:
Bennett, D. (2018, December 1). The Most Common Chord Progression in Japan? [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=524_2y32Skg
Hook, A. (2020). Hooktheory I: The Aural Approach to Music Theory. Hooktheory Press.
VanDerWerff, T. (2019, December 19). How a single chord progression unites anime, J-pop, and video games. Vox. Retrieved from https://www.vox.com/culture/2019/12/19/21013289/japanese-chord-progression-anime-jpop-video-games-iv-v-iii-vi
