Mastering the Altered Dominant (7alt) Chord: A Comprehensive Guide
What is an Altered Dominant (7alt) Chord?
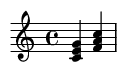
The altered dominant, commonly notated as 7alt, is a sophisticated dominant 7th chord that incorporates one or more altered extensions (b9, #9, b5, #5) to create maximum harmonic tension. This chord is a staple in jazz harmony and appears frequently in classical and contemporary music when composers want to intensify the resolution to the tonic.
Historical Context and Musical Significance
The altered dominant emerged prominently during the bebop era (1940s) as jazz musicians like Charlie Parker and Dizzy Gillespie sought more dissonant, colorful sounds. The chord's tension-filled quality makes it perfect for:
- Creating dramatic resolutions in classical cadences
- Adding chromatic interest in jazz standards
- Intensifying rock/pop progressions
Technical Construction
Chord Formula
The basic altered dominant formula builds on a dominant 7th chord (1-3-5-b7) with alterations:
- Root: Foundation tone (e.g., G in G7alt)
- 3rd: Major 3rd (defines dominant quality)
- b7: Minor 7th (essential for dominant sound)
- Alterations: b5/#5 and/or b9/#9
Common Voicings
Piano (left hand): G-B-F-Ab (root-3rd-b7-b9)
Guitar: 3x344x (F-B-Eb-Ab, using tritone substitution)
Practical Applications
Jazz Progressions
II-V-I with altered dominant:
Dm7 | G7alt | CMaj7
Classical Usage
Chopin's Prelude in E Minor uses altered dominants to heighten emotional impact before resolving to minor tonic chords.
Progressive Exercises
Level 1: Identification
Play C7, then C7alt - notice the added tension from alterations.
Level 2: Voice Leading
Resolve G7alt (G-B-F-Ab) to CMaj7 (C-E-G-B) with smooth motion.
Level 3: Improvisation
Use G altered scale (G-Ab-Bb-B-Db-Eb-F) over G7alt chords.
Genre Examples
- Jazz: Coltrane's Giant Steps (rapid altered dominants)
- Rock: Muse uses altered dominants for dramatic effect
- Film Music: Hans Zimmer's tense harmonic moments
Historical Context and Musical Significance
The altered dominant chord emerged during the late Romantic period as composers like Wagner and Debussy pushed harmonic boundaries. Its significance skyrocketed in the bebop era (1940s-50s) when jazz musicians like Charlie Parker and Dizzy Gillespie exploited its tension-resolution properties to create chromatic fluidity. The 7alt chord represents the culmination of dominant chord evolution - where every non-essential tone (9th, 11th, 13th) is altered to maximize harmonic tension before resolution.
Musically, the chord serves two critical functions: it creates maximum dissonance against tonic resolution points (V-I cadences), and enables smooth voice leading in modulations. The altered extensions (b9, #9, #11, b13) provide all possible chromatic approaches to tonic chord tones. This harmonic intensity made it indispensable in jazz harmony, film scoring (Bernard Herrmann's Psycho shower scene), and progressive rock (King Crimson's 21st Century Schizoid Man).
Progressive Exercises
Beginner
Practice shell voicings with altered tensions:
- RH: E♭+B♭ (3rd+b7) | LH: G (root)
- Add one alteration: RH: E♭+B♭+C♯ (3rd+b7+#9)
Intermediate
Cycle of fifths progression with alterations:
- | Dm7 | G7♭9♯11 | Cmaj7 | F♯7♭13 |
- | Bm7 | E7♯9 | Amaj7 | A♭7alt |
Advanced
Reharmonization challenge:
- Take standard Autumn Leaves progression
- Replace all V7 chords with appropriate altered variants
- Improvise using altered scale (G7alt: G-A♭-B♭-B♯-D♭-E♭-F)
Ear Training Tips
Develop recognition through targeted drills:
- Interval Identification: Isolate altered tensions (b9 = minor 2nd, ♯9 = minor 3rd, ♭13 = minor 6th)
- Chord Quality Comparison: Contrast G7 vs. G7♭9 vs. G7♯9. Note how alterations increase dissonance
- Resolution Recognition: Practice identifying V7alt → I cadences in jazz standards (e.g., Moment's Notice by Coltrane)
- Transcription Exercise: Transcribe McCoy Tyner's solo on "A Love Supreme" focusing on altered dominant usage
Use apps like EarMaster for customized drills: Set chord progression "ii - V7alt - I" with randomized alterations. Start with slow tempos (60bpm) increasing to 200bpm.
Common Usage in Different Genres
Jazz
Primary tension builder in ii-V-I progressions. Herbie Hancock's "Maiden Voyage" uses F7alt (E♭-G-A-D) for modal ambiguity. Bebop players employ altered dominants for chromatic passing chords.
Fusion
Extended alterations as tonal centers. Chick Corea's "Spain" features D7♯9♭13 as primary harmony. Often voiced with quartal harmony (C-F-B-E for G7alt).
Film Scoring
Dramatic tension in horror/suspense. Hans Zimmer's "Joker Theme" uses B♭7alt with low brass clusters. Typically resolves deceptively to vi instead of I.
Progressive Rock
Rhythmic displacement tool. Dream Theater's "The Dance of Eternity" features E7♭9 in 19/16 time. Often paired with synth textures.
Neo-Soul
Extended altered voicings in upper structures. Robert Glasper's "Black Radio" uses G7(♯9♭13) as Fm/A♭ polychord. Frequently appears in turnarounds.
Online Resources
- Jazz at Lincoln Center's "Jazz Academy" YouTube series (altered dominant masterclasses)
- OpenMusicTheory.com - Altered Dominant Chapter (interactive exercises)
- JazzAdvice.com - "Ultimate Guide to Altered Dominants" (practice routines)
Academic Studies
- "The Evolution of Dominant Harmony in Jazz" - Journal of Jazz Studies Vol. 12
- "Altered Dominants in Post-Tonal Theory" - Music Theory Spectrum 2020
