The Half Diminished Chord: A Complete Guide for Musicians
What is a Half Diminished Chord?
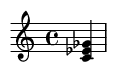
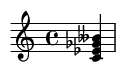
A half diminished chord, also known as a minor seventh flat five (m7♭5), is a four-note chord consisting of:
- Root
- Minor third
- Diminished fifth
- Minor seventh
The chord formula is: 1 - ♭3 - ♭5 - ♭7
Historical Context and Musical Significance
Emerging in the Romantic era, half diminished chords became crucial in:
- Classical music as predominant chords
- Jazz standards as iiØ7 chords in minor keys
- Film scoring for mysterious/dramatic effects
Technical Construction
Interval Structure
- Root to ♭3: Minor 3rd (3 semitones)
- ♭3 to ♭5: Minor 3rd (3 semitones)
- ♭5 to ♭7: Major 3rd (4 semitones)
Common Voicings
Piano: BØ7 = B-D-F-A (closed position)
Guitar: X2323X (BØ7 in drop 2 voicing)
Practical Applications
In Jazz
As the ii chord in minor ii-V-i progressions:
BØ7 - E7 - Am7
In Classical Music
As predominant harmony leading to dominant:
ii× - V7 - I
Progressive Exercises
Level 1: Identification
Play CØ7 (C-E♭-G♭-B♭) in all inversions
Level 2: Progressions
Practice ii×-V7-I in all minor keys
Level 3: Substitutions
Replace dominant chords with ×9 chords
Genre Applications
Jazz
Used extensively in standards like "Autumn Leaves"
Rock/Pop
Creates tension in progressions (e.g., Radiohead)
Classical
Essential in Romantic era chromatic harmony
