Major Seventh Chord: The Jazz Standard of Sophistication

b4n1
May 25, 2025, 2:22 a.m.
Major Seventh Chord: The Jazz Standard of Sophistication
Summary:
The major seventh chord adds sophistication and color to basic major triads by including the major seventh interval. This elegant harmony is fundamental to jazz, bossa nova, and contemporary music, creating a dreamy, sophisticated sound that's both stable and harmonically rich.
Keywords:
Major seventh chord, maj7, jazz harmony, sophisticated harmony, extended chord, major seventh interval, tonic function, bossa nova, smooth jazz, chord color.
Introduction:
The major seventh chord represents one of the most beautiful and sophisticated harmonies in Western music. By adding the major seventh interval to a basic major triad, this chord creates a lush, dreamy sound that has become synonymous with jazz, bossa nova, and contemporary popular music.
Unlike the dominant seventh chord with its strong resolution tendency, the major seventh chord provides stability while adding harmonic color, making it perfect for establishing tonic harmony in jazz and creating sophisticated harmonic textures in various musical styles.
Structure and Construction:
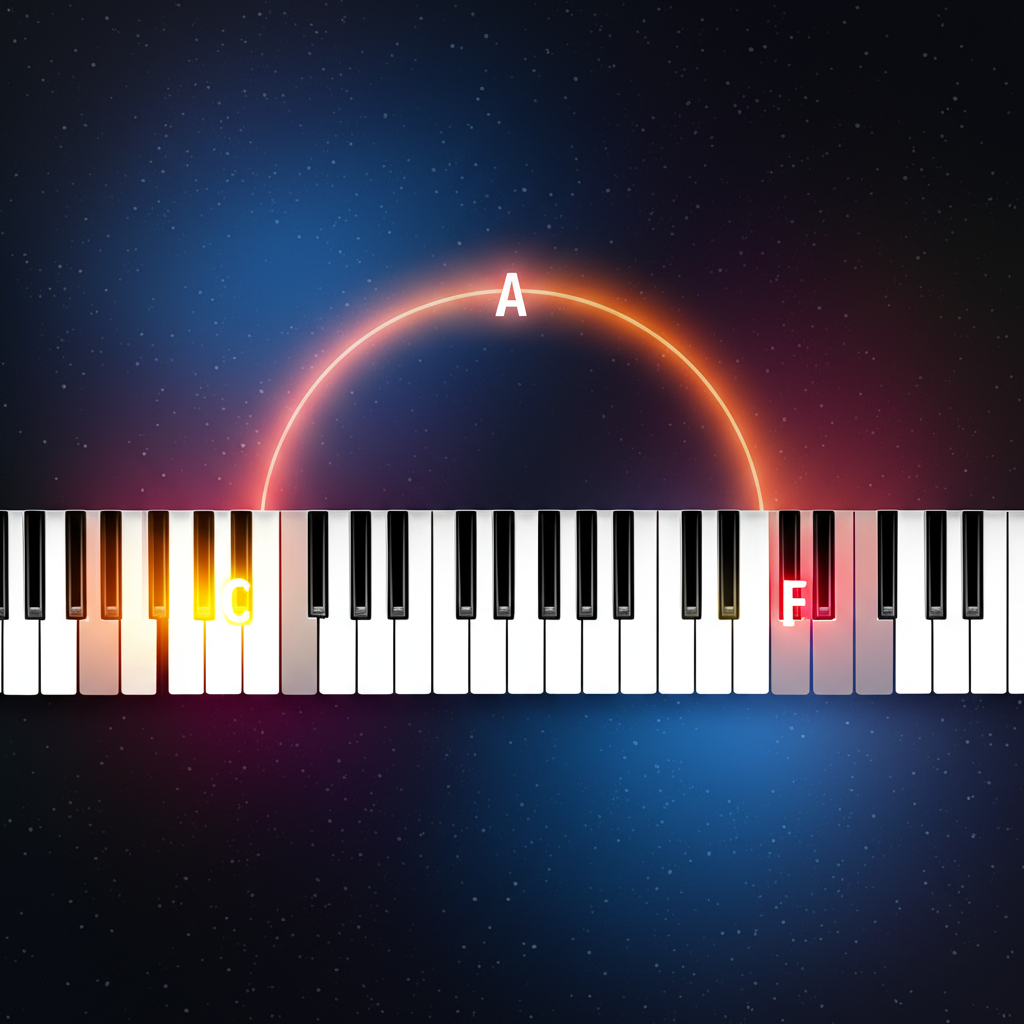
A major seventh chord consists of:
- Root: The fundamental note
- Major third: 4 semitones above the root
- Perfect fifth: 7 semitones above the root
- Major seventh: 11 semitones above the root
C Major Seventh Chord:
Formula: 1 - 3 - 5 - 7
Notes: C - E - G - B
Intervals: Major 3rd, Perfect 5th, Major 7th
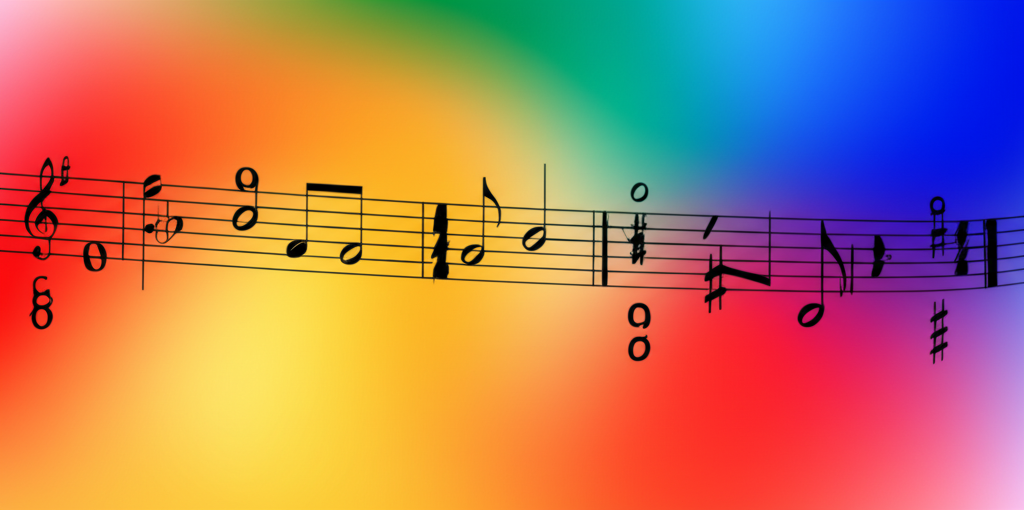
Examples:
C Major Seventh Chord:
Notación musical:
Major Seventh Progression:
Notación musical:
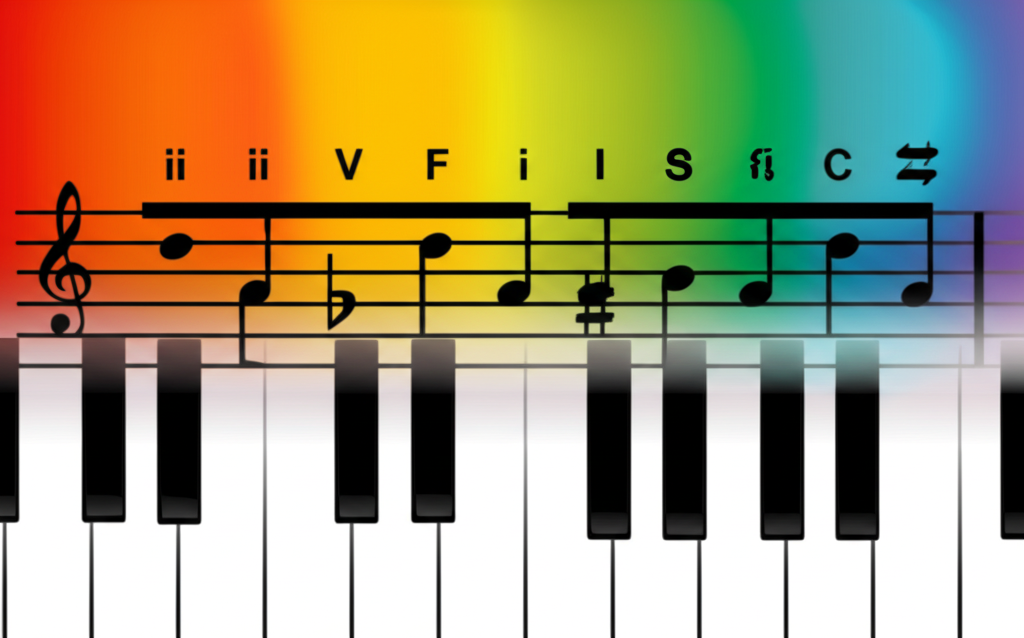
Jazz ii-V-I with Major Seventh:
Notación musical:
Harmonic Function:
Tonic Function:
Major seventh chords often serve as sophisticated tonic chords:
- Provide stable resolution in jazz progressions
- Create rich, colorful harmony without tension
- Establish key center with added sophistication
- Substitute for simple major triads in contemporary styles
Subdominant Function:
Can also function as subdominant harmony:
- IVmaj7 chords in major keys
- Creates smooth voice leading to dominant chords
- Adds color to traditional I-IV-V progressions
Jazz Applications:
Major seventh chords are fundamental to jazz harmony:
- Standards: Essential in jazz standard chord progressions
- Comping: Perfect for piano and guitar accompaniment
- Ballads: Create lush, romantic harmonic textures
- Bossa nova: Signature sound of Brazilian jazz
- Smooth jazz: Cornerstone of contemporary jazz styles
Voicing and Inversions:
Close Voicings:
All chord tones within an octave:
- Root position: C-E-G-B
- First inversion: E-G-B-C
- Second inversion: G-B-C-E
- Third inversion: B-C-E-G
Open Voicings:
Spread chord tones across multiple octaves for richer sound.
Drop Voicings:
Lower certain chord tones by an octave for better voice leading and spacing.
Different Voicings:
Famous Songs Using Major Seventh Chords:
Countless classic songs feature major seventh harmony:
- "Fly Me to the Moon" - Frank Sinatra
- "Girl from Ipanema" - Antonio Carlos Jobim
- "The Way You Look Tonight" - Jazz standard
- "Don't Know Why" - Norah Jones
- "Autumn Leaves" - Jazz standard
- "All of Me" - John Legend
Chord Progressions:
Jazz ii-V-I:
The fundamental jazz progression often uses major seventh tonic:
Dm7 - G7 - Cmaj7
Circle of Fifths:
Major seventh chords work beautifully in circle progressions:
Cmaj7 - Fmaj7 - Bbmaj7 - Ebmaj7
Contemporary Pop:
Modern pop songs often use major seventh chords for sophistication:
Cmaj7 - Am7 - Fmaj7 - G7
Instrumental Techniques:
Piano:
Piano techniques for major seventh chords:
- Shell voicings (root, third, seventh)
- Rootless voicings for comping
- Block chord techniques
- Spread voicings across both hands
Guitar:
Guitar applications:
- Moveable chord shapes
- Fingerstyle arpeggiation
- Jazz rhythm guitar comping
- Barre chord variations
Voice Leading:
Smooth connections between major seventh chords using common tones and step-wise motion.
Emotional Character:
Major seventh chords evoke specific feelings:
- Sophistication: Add elegance to simple progressions
- Dreaminess: Create floating, ethereal quality
- Warmth: Provide rich, enveloping harmony
- Stability: Offer resolution without harshness
- Romance: Perfect for ballads and love songs
Comparison with Other Seventh Chords:
vs. Dominant Seventh:
Major seventh is stable; dominant seventh seeks resolution.
vs. Minor Seventh:
Major seventh is brighter; minor seventh is more subdued.
vs. Half-Diminished:
Major seventh is consonant; half-diminished is tense and unstable.
Learning and Practice:
Ear Training:
Developing recognition skills:
- Listen for the characteristic "dreamy" quality
- Compare with major triads to hear the added color
- Practice identifying in jazz recordings
- Learn to hear the major seventh interval
Practice Exercises:
Building technique:
- Practice all inversions in multiple keys
- Work on smooth voice leading between chords
- Learn common progressions using major sevenths
- Experiment with different voicings and spacings
Contemporary Applications:
Neo-Soul:
Major seventh chords are essential in neo-soul and R&B.
Lo-Fi Hip Hop:
Often sampled in lo-fi beats for their warm, nostalgic quality.
Indie Pop:
Used to add sophistication to simple pop progressions.
Film Scoring:
Perfect for romantic, dreamy, or contemplative scenes.
Common Mistakes:
- Overuse: Too many major sevenths can sound clichéd
- Poor voice leading: Not considering smooth chord connections
- Wrong context: Using in styles where they don't fit
- Muddy voicings: Poor spacing creating unclear harmony
Extensions and Variations:
Major Ninth:
Adding the ninth creates even richer harmony (Cmaj9).
Major Thirteenth:
Full extension with ninth, eleventh, and thirteenth (Cmaj13).
Add9:
Major triad with added ninth, no seventh (Cadd9).
Cultural Impact:
Major seventh chords have significantly influenced popular music:
- Defined the sound of jazz and bossa nova
- Brought sophistication to popular music
- Influenced R&B, soul, and contemporary styles
- Became standard in film and television scoring
Fun Facts:
- The major seventh chord was considered dissonant in classical music but became acceptable in jazz.
- Debussy was one of the first classical composers to use major seventh chords extensively.
- The chord appears naturally in the harmonic series as the relationship between certain overtones.
- Many elevator music and smooth jazz pieces rely heavily on major seventh harmony.
- The major seventh interval creates a distinctive "floating" quality when played high in the chord.
Conclusions:
The major seventh chord represents a perfect balance between stability and sophistication in harmonic language. Its ability to provide tonic function while adding rich harmonic color has made it indispensable in jazz, contemporary popular music, and film scoring.
Understanding major seventh chords opens the door to more sophisticated harmonic thinking and provides essential tools for composition, arrangement, and performance in contemporary musical styles. Whether you're playing jazz standards, writing pop songs, or scoring films, mastering major seventh harmony will enhance your musical vocabulary and expressive capabilities.
The enduring popularity of major seventh chords across multiple genres demonstrates their unique ability to add elegance and sophistication while maintaining harmonic stability, making them one of the most valuable tools in the modern musician's harmonic toolkit.